Identity and access management is for making sure that only the right people can access an organization's data and resources. It's a cybersecurity practice that enables IT administrators to restrict access to organizational resources so that only the people who need access have access. IAM is a critical framework within information security that manages digital identities and controls access to an organization's resources.
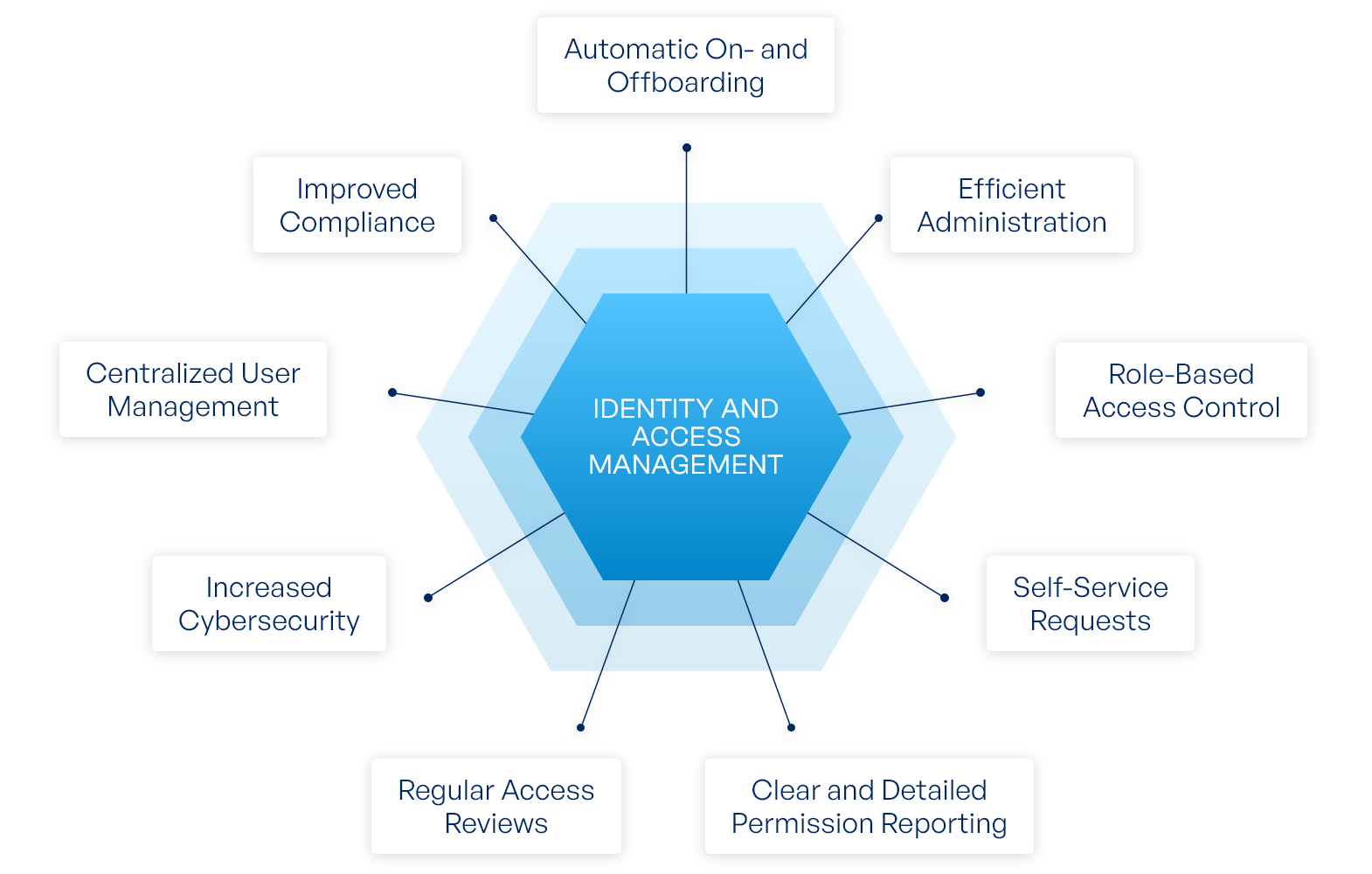
Core Components of IAM include:
Identity (User) Management: This involves creating, maintaining, and deleting user identities. It includes:
- User provisioning and deprovisioning
- Identity lifecycle management
- Self-service portals for users to manage their own accounts
Access Management: This controls what resources users can access. Key aspects include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
- Least privilege principle implementation
Authentication: Authentication is the process of verifying a user's identity. It ensures that users are who they claim to be before granting access to resources.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Biometric authentication
Authorization: Determines what actions authenticated users can perform within a system.
Auditing and Reporting: Tracks user activities and generates reports for compliance and security analysis.
IAM's Role in Information Security
IAM plays a crucial role in protecting an organization's information assets:
- Reducing Attack Surface: By implementing the principle of least privilege, IAM limits the potential damage from compromised accounts.
- Enhancing Compliance: IAM helps organizations meet regulatory requirements by controlling and auditing access to sensitive data.
- Improving User Experience: Features like SSO reduce password fatigue and improve productivity while maintaining security.
- Enabling Secure Remote Access: As workforces become more distributed, IAM provides secure access to resources from any location.
- Automating Security Processes: IAM automates many security tasks, reducing human error and improving efficiency.
Statistics on Breaches Involving Stolen Credentials
The use of stolen credentials in data breaches is alarmingly common:
- According to the Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, 74% of all breaches involve the human element, including the use of stolen credentials.
- The same report states that 86% of breaches for Basic Web Application attacks involved the use of stolen credentials as initial access.
- IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 found that stolen or compromised credentials were responsible for 16% of breaches, with an average cost of $4.9 million per breach.
- A SpyCloud report revealed that 61% of data breaches in 2023, involving over 343 million stolen credentials, were infostealer malware-related.
- The Identity Theft Resource Center reported 3,122 publicly reported data breaches in 2023, impacting 349 million people.
- According to LexisNexis Risk Solutions, 1 in every 11 new account creations are attacks, often using stolen credentials.
- SpyCloud's analysis found that the average identity appears in as many as nine breaches and is associated with 15 breach records.
These statistics underscore the critical importance of robust IAM systems in protecting against credential-based attacks. By implementing strong authentication methods, regularly updating access controls, and monitoring for suspicious activities, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to breaches involving stolen credentials.
To find out more about how we can resolve your IT issues please email or call us:
Send us an email Call us +44 (0)1462 416400













